'While it May Sound Futuristic, It Holds Great Promise': Olga Dragoy Shares Her Thoughts on Language Function Restoration and the Future of Neurotechnology
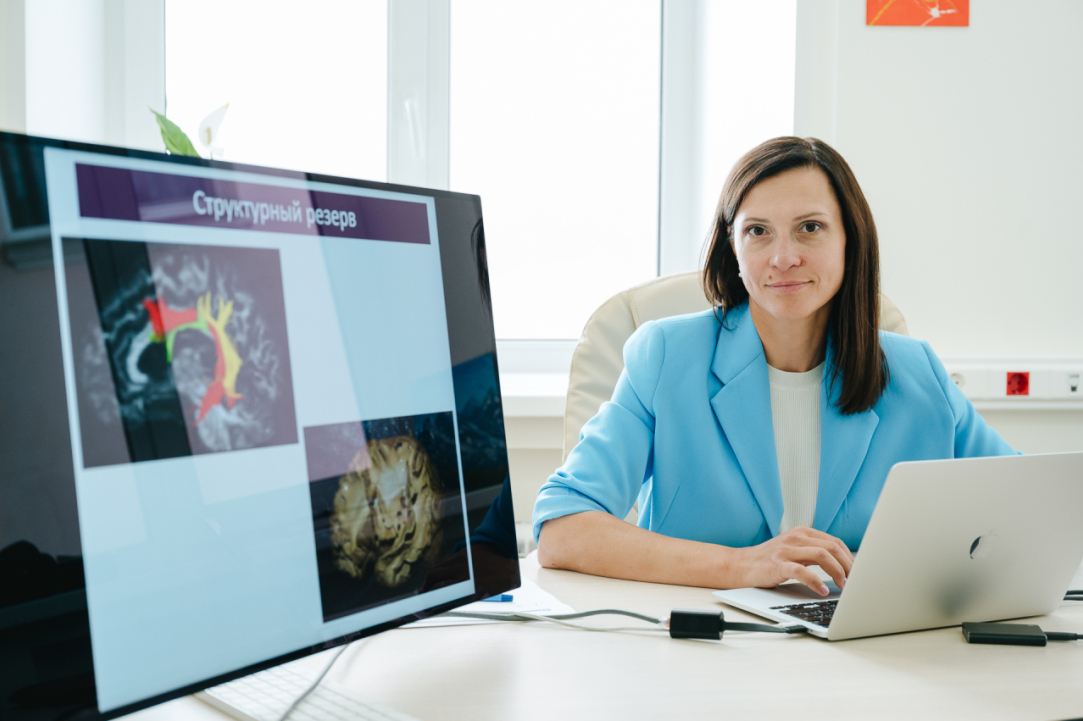

In the spring of 2023, the fifth strategic project of the Priority 2030 programme, 'Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment,' was launched at HSE University. The strategic project brings together researchers from all campuses of HSE University. In her interview with the HSE News Service, Olga Dragoy, head of the strategic project and Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, shares an overview of the advanced technologies neuroscientists are creating today, the underlying inspiration driving these efforts, and the operational dynamics of interdisciplinary applied projects.
From Conducting Basic Research to Helping Patients
I believe that all of us who have joined the large team of the strategic project this year have reached a point in our research where we are compelled to venture into creating tangible, applied solutions, such as tools which can be used immediately to benefit people. Our centre has already started developing such solutions: this summer, we successfully launched HSE University's first application on RuStore—it is designed for diagnosing language disorders in children (KORABLIK, a Russian acronym for Clinical Assessment of Basic Linguistic Competencies). It is the culmination of five years of foundational work, followed by several more years dedicated to translating the results into a user-friendly application.
The strategic project 'Human Brain Resilience' implemented by the Centre for Language and Brain comprises two major areas of focus. The first one concerns neural interfaces and digital tools for treating language disorders. During the ten years that the centre has been operating within HSE University, we have gained extensive insights into the mechanisms of various language disorders in both adults and children. Now, we are ready to propose tools for treating these disorders. It is undoubtedly a technological challenge, as we need to acquire new expertise and establish new partnerships. The second area of focus involves formulating clinical protocols to aid in the recovery of language function after stroke through a combination of brain stimulation and evidence-based speech therapy programmes.
EEG-Based Neural Interfaces
This year, we have started a collaboration with the Chen Frontier Lab for Applied Neurotechnology in China. The team of Dr Gerwin Schalk at the Chen Frontier Lab has developed an inexpensive and easy-to-use EEG device with four electrodes. By way of comparison, similar EEG systems typically incorporate 64 or more electrodes. A device the size of a mobile phone is affixed to a person’s head to read the electrical activity of their brain. Based on this technology, we have been developing a neural computer interface in Russian for the treatment of a specific language disorder: aphasia. A treatment scheme has been formulated, and corresponding linguistic material has been selected and programmed. Currently, we are integrating our software solutions with the EEG system.

This development will help medical practitioners and patients manage anomia—the most common symptom in all types of aphasia, where individuals have difficultly retrieving words for naming objects during spontaneous speech. For example, they may say 'box' instead of 'basket' or use a word that sounds similar to 'basket,' such as 'bicycle.'
Instead of cumbersome and costly installations that require patients to wear caps with numerous electrodes and involve complex algorithms, we will be able to offer a compact and relatively user-friendly device.
This winter, we will conduct tests on healthy volunteers. Next year, we plan to involve patients, and by the end of 2024, we expect to deliver a tangible outcome: a hardware and software complex ready for use by any medical practitioner.
'While It May Sound Futuristic, It Holds Great Promise'
Individuals with specific neurogenic injuries may find themselves unable to speak aloud, yet they retain the ability to generate words and sentences internally. This indicates that their inner speech remains intact. The reasons for this condition can vary, including, among others, disorders in the conductive pathways and articulatory atrophy.
One way to assist such patients is through the use of electrode arrays surgically implanted on the cerebral cortex. These arrays can register electrical signals in the brain, so that the signals may be subsequently translated into sounds or written text using language models.
Globally, efforts are underway to expand dictionaries for training machine learning models not just on individual words, but on entire sentences. Three years ago, researchers from the UK were the first to publish their results; their model demonstrated the ability to recognise 50 individual words. Mind reading is still a distant prospect, but an early step in this direction has been taken. Language models will contribute to expanding vocabulary and progressing from single-word reconstruction to generating complete sentences. In this area, we collaborate with a team of computational linguists at HSE University led by Olga Lyashevskaya, author of the frequency dictionary of the Russian language.

This may sound like science fiction, but experiments are underway and some progress has been achieved. Until now, processing speed has been the primary challenge for all such technologies. Invasive EEG-based neuroprostheses are currently slow and challenging for routine practical use.
I can see enormous fundamental benefits to be gained from research in this area. The technology we are referring to does not require physical effort. Through the implantation of electrodes into the cerebral cortex, we can use specific algorithms to reconstruct the language function. Speech does not have to be confined to articulated sounds; it could be encoded in ones and zeros and transmitted to another person, virtually anywhere. I believe that it holds great promise, although it may sound futuristic. If successful, we will be able to transmit internal speech without words, creating a new communication channel.
I am not sure whether healthy individuals would consent to be implanted with electrodes. This innovative communication channel must first demonstrate its effectiveness in patients who need it. The horizon of my expectations regarding this technology lies within the next 10 to 20 years.
Preparing for Future Technologies: Language Mapping
Meanwhile, we are making preparations for the introduction of these futuristic technologies. We are learning to identify, accurately and promptly, the brain’s electrical activity in connection with various aspects of language function.
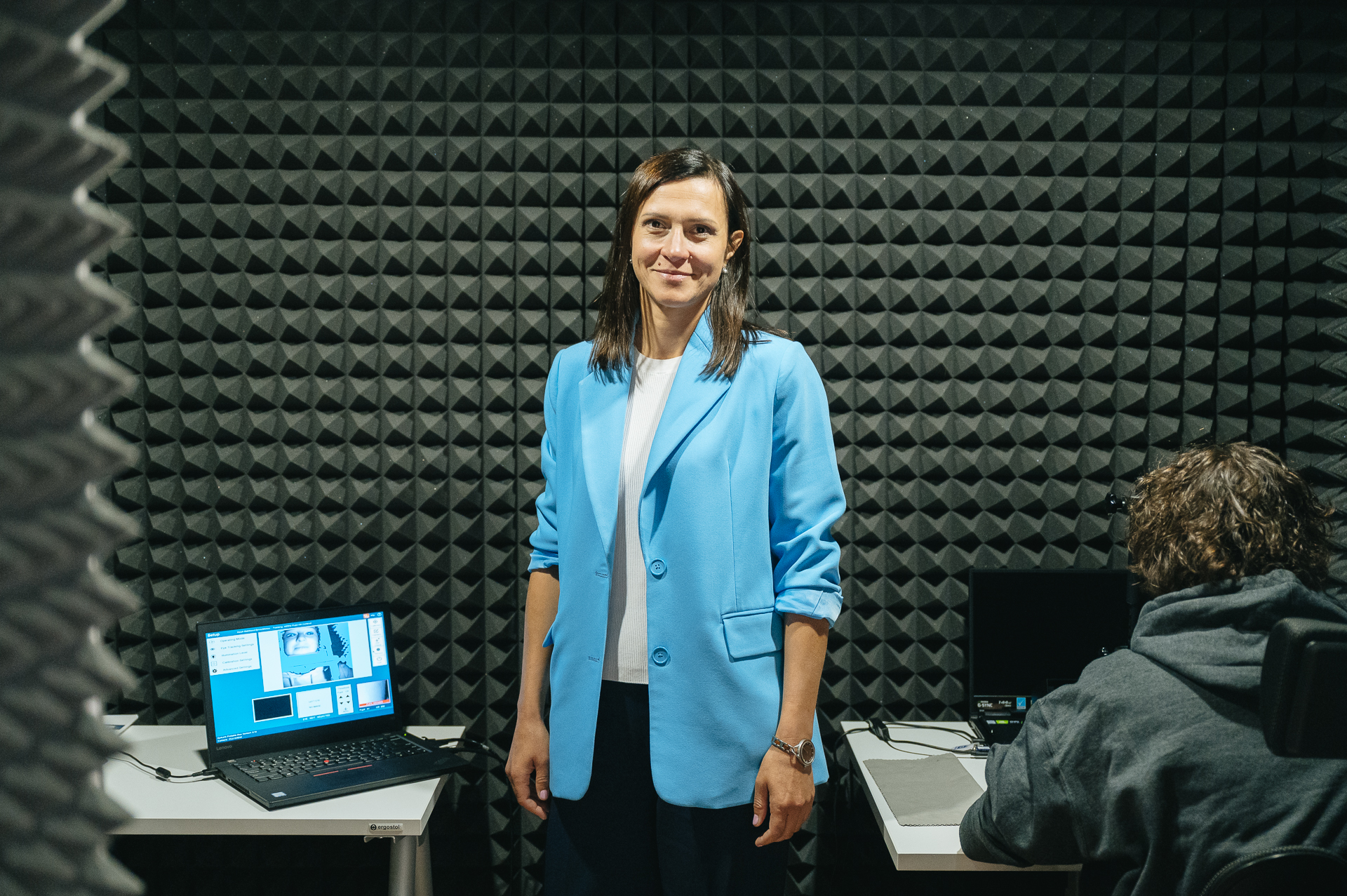
We are working on this in parallel with Alexey Ossadtchi's team at the Centre for Bioelectric Interfaces. Specifically, we have been conducting research on patients with electrode arrays implanted in their brains for medical reasons. These patients participate in various language-related tasks, such as naming objects in pictures, repeating words, and undergoing listening tests. Meanwhile, we map precisely where the electrical signals associated with these language activities occur. Our team of neurolinguists has been designing speech paradigms (linguistic tasks) that facilitate effective language mapping in different regions of the brain. We then compare language maps for each task to determine which aspect of language function is realised in different parts of the brain, such as the frontal, temporal, or parietal lobes.
Therapy in a Game Format
Additionally, in collaboration with HSE linguists, we have developed a therapeutic tablet application—a digital game designed to help alleviate anomia (the problem with word selection which I mentioned earlier) in post-stroke patients. A patient views pictures of objects on the tablet and is instructed to name them. When the answer is correct, an arrow displayed on the screen hits the target; if the answer is not quite accurate, the arrow falls near the target; and if the patient’s answer is completely off the mark, the arrow misses the target.
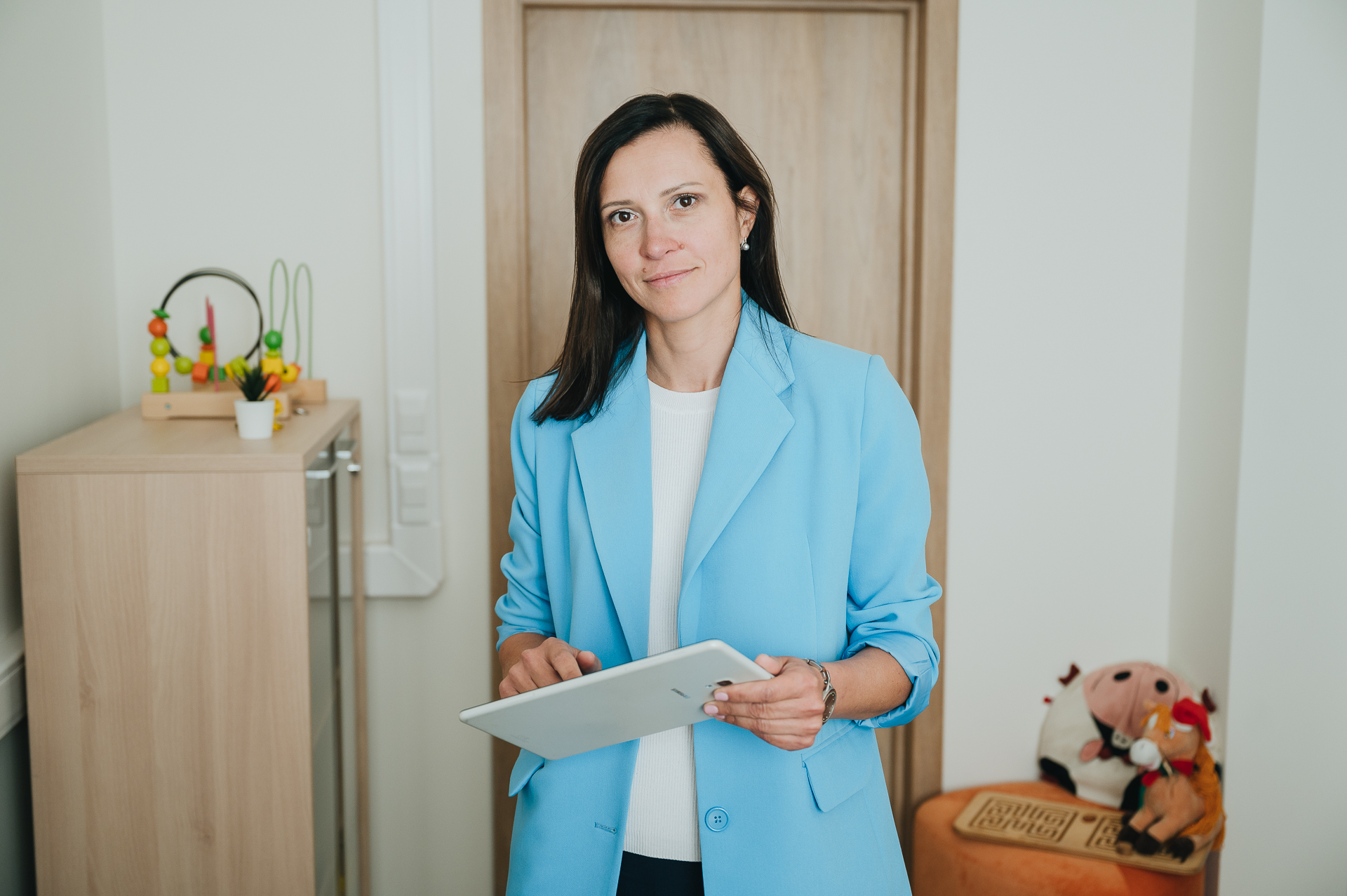

Such feedback training lies at the core of any well-designed therapy. However, even the most advanced clinical institutions offer such treatment for a maximum of three weeks, while our application can be downloaded and used for practice as much as one desires. As of now, it is the only gaming application worldwide designed to address language disorders.
Helping Stroke Patients through Brain Stimulation
A segment of our team, led by Olga Buivolova, has been working on restoring language function through non-invasive brain stimulation, using methods such as transcranial electrical stimulation (micropolarisation) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Strokes affecting the left hemisphere, where language function is predominantly localised, are of particular interest, as damage to this area is what leads to aphasia.
A stroke causes an imbalance of activity between the hemispheres. The left hemisphere is suppressed, while the right hemisphere, following the laws of nature, is, conversely, overexcited. Approximately 20 years ago, scientists proposed the idea of slowing down the right hemisphere to restore activity to the functioning areas in the left hemisphere. This idea is compelling and has been supported by the majority of scientists. In reality, however, it proves effective in only 50% of patients. The question is, why? Our hypothesis is that the success or failure of this approach depends on the amount of preserved brain matter in the left hemisphere. With a certain size of brain lesion, this approach can be productive and effective, and activity can be restored, but not with a different size.

To find an answer to this question, we are investigating the association between successful left hemisphere recovery and the residual neural substrate in language processing areas. The metric for this residual neural substrate is the volume of the arcuate fasciculus, a white matter bundle around which the entire language system is constructed.
The arcuate fasciculus connects the language processing areas in the frontal lobe with the temporal and parietal lobes. There is a hypothesis suggesting that individual language processing zones are precisely located where this bundle enters the cortex. In other words, the bundle enters there to facilitate the connection of different language processing zones, thereby ensuring the operation of the entire language network in the brain. This means that the structure reflects the function.
The anatomy of the arcuate fasciculus is well-known; therefore, by measuring its residual volume (in cubic millimetres) using tractography, we can reasonably predict whether it makes sense to use this type of therapy with a particular patient.
We are currently conducting a clinical trial with groups of patients who have varying volumes of the arcuate fasciculus. One group is receiving speech therapy with stimulation, another is receiving therapy without stimulation, and the third is receiving only stimulation without therapy. This will enable us to understand the main factor in successful language function recovery—whether it is the amount of preserved brain matter for language processing in the left hemisphere, the application of TMS, or the application of speech therapy. Once we determine this, we can translate our findings into technology by implementing a clinical protocol for the treatment of aphasia, providing clear indications of who will and will not benefit from this treatment.
See also:
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
Advancing Personalised Therapy for More Effective Cancer Treatment
Researchers from the International Laboratory of Microphysiological Systems at HSE University's Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology are developing methods to reduce tumour cell resistance to drugs and to create more effective, personalised cancer treatments. In this interview with the HSE News Service, Diana Maltseva, Head of the Laboratory, talks about their work.
Master’s Students of HSE, University of Campinas, and Tsinghua University Publish Joint Student Research Collection
Master’s students of the HSE ISSEK programme ‘Science, Technology and Innovation Management and Policy’ have released a joint research collection with the University of Campinas (Brazil) and Tsinghua University (China) titled ‘Being Innovative or Being on the Safe Side—Managing the Risk of Failure.’ The authors explore how organisations perceive risks and embrace innovation within different cultural contexts.
‘A Turn Away from Stereotypes’: Moscow Hosts ‘Researching the Deaf Community’ Conference
On October 17–19, 2025, the third annual interdisciplinary conference ‘Researching the Deaf Community 2025: on the Periphery of Attention’ took place at GES-2 House of Culture in Moscow. The event was organised with the participation of the HSE International Laboratory for Social Integration Research. HSE University Vice Rector Irina Martusevich addressed attendees at the opening ceremony.
Exploring the Mind: HSE Scientists Discuss Cognitive Technologies of the Future
Why we make irrational decisions, how the brain responds to fakes, and whether neural networks are capable of thinking—these were the topics discussed by early-career scientists of HSE University during the NAUKA 0+ science festival. The event brought together students and experts from various fields, united by a common goal—to deepen their understanding of the human brain and cognitive technologies.
HSE Researchers Assess Creative Industry Losses from Use of GenAI
Speaking at the IPQuorum.Music forum on October 15, Leonid Gokhberg, HSE First Vice Rector, and Daniil Kudrin, an expert at the Centre for Industry and Corporate Projects of HSE ISSEK, presented the findings of the first study in Russia on the economic impact of GenAI on creative professions. The analysis shows that creators’ potential losses could reach one trillion roubles by 2030.